| previous |
|

![]() Move
the mouse before the first line in the main function. Then push
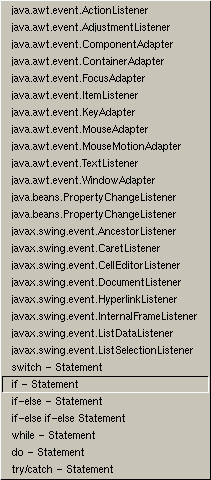
(not release) the rightmost icon in the toolbar. It shows a capital A
and some arrows pointing downwards. A menu will pop up listing a choice
of structures. Select the 'if statement'.
You can see that a template for an 'if statement'
has been created in your editor window. Move the last curly bracket behind
you System.println line so that is part of the if clause.
Then add a condition between the parentheses. Let us use '(!args[0].equals("quiet"))'.
Move
the mouse before the first line in the main function. Then push
(not release) the rightmost icon in the toolbar. It shows a capital A
and some arrows pointing downwards. A menu will pop up listing a choice
of structures. Select the 'if statement'.
You can see that a template for an 'if statement'
has been created in your editor window. Move the last curly bracket behind
you System.println line so that is part of the if clause.
Then add a condition between the parentheses. Let us use '(!args[0].equals("quiet"))'.
 Maybe
you have just forgotten what 'equals' exactly does (why not use
'==' ?). It happens sometimes that people remember names of classes and
methods, but not the details of how they are used (e.g. order of arguments).
Therefore Jedi provides an easy to use help feature. Before we can
use this, it needs to be configured, though. Select 'JavaDoc
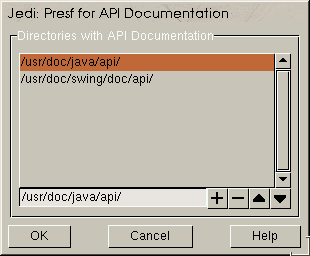
API Directories' in the 'Prefs'
menu. A window will appear that lets you configure where your documentation
for JDK and other Java packages are located. Move the mouse over
the list field, push the right button and select 'Add
using requester'. Then direct the requester to the api
subdirectory in your java installation: <javadir>/doc/api.
When you click 'Ok' Jedi will start
to build a help index, which should take a few seconds.
Maybe
you have just forgotten what 'equals' exactly does (why not use
'==' ?). It happens sometimes that people remember names of classes and
methods, but not the details of how they are used (e.g. order of arguments).
Therefore Jedi provides an easy to use help feature. Before we can
use this, it needs to be configured, though. Select 'JavaDoc
API Directories' in the 'Prefs'
menu. A window will appear that lets you configure where your documentation
for JDK and other Java packages are located. Move the mouse over
the list field, push the right button and select 'Add
using requester'. Then direct the requester to the api
subdirectory in your java installation: <javadir>/doc/api.
When you click 'Ok' Jedi will start
to build a help index, which should take a few seconds.
![]() Now we
are ready to test the help feature. Move the mouse over the text editor
and click on the word 'equals' you just typed. The textcursor
will appear there. Now click the help icon. It shows an open book and a
questionmark. Jedi will highlight the whole word 'equals'
and open a window that displays help text.
Now we
are ready to test the help feature. Move the mouse over the text editor
and click on the word 'equals' you just typed. The textcursor
will appear there. Now click the help icon. It shows an open book and a
questionmark. Jedi will highlight the whole word 'equals'
and open a window that displays help text.
| previous |
|